Discriminant analysis can be more easily understood from plots of the data variables showing how observations are classified.
plot_discrim() uses the ideas behind effect plots (Fox, 1987): Visualize predicted classes of the observations for two focal variables over a
grid of their values, with other variables in a model held fixed. This differs from the usual effect plots in that the predicted
values to be visualized are discrete categories rather than quantitative.
In the case of discriminant analysis, the predicted values are class membership,
so this can be visualized by mapping the categorical predicted class to discrete colors used as the background for the plot, or
plotting the contours of predicted class membership as lines (for MASS::lda()) or quadratic curves (for MASS::qda()) in the plot.
The predicted class of any observation in the space of the variables displayed can also be rendered as colored tiles or points
in the background of the plot.
plot_discrim() also allows you to visualize the classification in discriminant space, of the weighted scores that best distinguish
among the groups. When there are only two discriminant dimensions, this view captures all the information regarding group separation
contained in all the predictors used in the lda() / qda() analysis. But, you can plot any pair of dimensions.
Usage
plot_discrim(
model,
vars,
data = insight::get_data(model),
resolution = 100,
point.size = 3,
showgrid = c("tile", "point", "none"),
contour = TRUE,
contour.color = "black",
tile.alpha = 0.2,
ellipse = FALSE,
ellipse.args = list(level = 0.68, linewidth = 1.2),
labels = FALSE,
labels.args = list(geom = "text", size = 5),
...,
other.levels
)Arguments
- model
a discriminant analysis model object from
MASS::lda()orMASS::qda()- vars
either a character vector of length 2 of the names of the
xandyvariables, or a formula of formy ~ xspecifying the axes in the plot. To plot in discriminant space, useLD2 ~ LD1,LD3 ~ LD2, etc.- data
data to use for visualization. Should contain all the data needed to use the
modelfor prediction. The default is to use the data used to fit themodel.- resolution
number of points in x, y variables to use for visualizing the predicted class boundaries and regions.
- point.size
size of the plot symbols use to show the data observations
- showgrid
a character string; how to display predicted class regions:
"tile"forggplot2::geom_tile(),"point"forggplot2::geom_point(), or"none"for no grid display.- contour
logical (default:
TRUE); should the plot display the boundaries of the classes by contours?- contour.color
color of the lines for the contour boundaries (default:
"black")- tile.alpha
transparency value for the background tiles of predicted class.
- ellipse
logical; if
TRUE, 68 percent data ellipses for the groups are added to the plot.- ellipse.args
a named list of arguments passed to
ggplot2::stat_ellipse(). Common arguments includelevel(confidence level, default: 0.68),linewidth(line thickness, default: 1.2),geom(either"path"for unfilled ellipses or"polygon"for filled ellipses), andalpha(transparency for filled ellipses). Any valid argument tostat_ellipse()can be used.- labels
logical; if
TRUE, class labels are added to the plot at the group means (default:FALSE).- labels.args
a named list of arguments passed to
ggplot2::geom_text()orggplot2::geom_label(). Common arguments includegeom(either"text"or"label", default:"text"),size(text size, default: 5),fontface(e.g.,"bold"or"italic"),nudge_xandnudge_y(position offsets), andalpha(transparency for label backgrounds). Any valid argument togeom_text()orgeom_label()can be used.- ...
further parameters passed to
predict()- other.levels
a named list specifying the fixed values to use for variables in the model that are not included in
vars(the non-focal variables). These values are held constant across the prediction grid. If not specified, the function uses sensible defaults: means for quantitative variables, and the first level for factors or character variables. For example, if your model includes variablesAge,Gender, andIncome, but you're plottingSepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width, you might specifyother.levels = list(Age = 30, Gender = "Female", Income = 50000)to generate predictions at those fixed values for the non-focal variables. This parameter is ignored when plotting in discriminant space (i.e., whenvarscontainsLD1,LD2, etc.).
Details
Since plot_discrim() returns a "ggplot" object, you can easily customize colors and shapes by adding scale layers after
the function call. You can also add other graphic layers, such as annotations, and control the overall appearance of
plots using ggplot2::theme() components.
Customizing colors and shapes
Use
ggplot2::scale_color_manual()andggplot2::scale_fill_manual()to control the colors used when usingshowgrid = "tile", because that maps both bothcolorandfillto the group variable.Use
ggplot2::scale_shape_manual()to control the symbols used forgeom_points(). Note that if there are more than 6 classes, you will need to use this, becauseggplotonly provides for 6 different shapes.
Customizing ellipses
The ellipse.args parameter provides fine control over the appearance of data ellipses. Common arguments include:
level: the confidence level for the ellipse (default: 0.68)linewidth: thickness of the ellipse line (default: 1.2)geom: either"path"for unfilled ellipses (default) or"polygon"for filled ellipses. (NB: at present, thefillaesthetic is not mapped to the class variable.)alpha: transparency when usinggeom = "polygon"
See ggplot2::stat_ellipse() for additional parameters.
Adding class labels
The labels and labels.args parameters allow you to add text labels for each class, positioned at the
group means. Common arguments for labels.args include:
geom: either"text"(default) for simple text or"label"for text with a background boxsize: text size (default: 5)fontface: font style such as"bold"or"italic"nudge_x,nudge_y: offsets for label positioningalpha: transparency for label backgrounds when usinggeom = "label"
See ggplot2::geom_text() and ggplot2::geom_label() for additional parameters.
Plotting in discriminant space
When vars specifies LD1 and/or LD2 (e.g., LD2 ~ LD1), the function automatically:
Calculates discriminant scores using
predict_discrim()Creates a new LDA model in discriminant space
Plots the observations and decision boundaries in that space
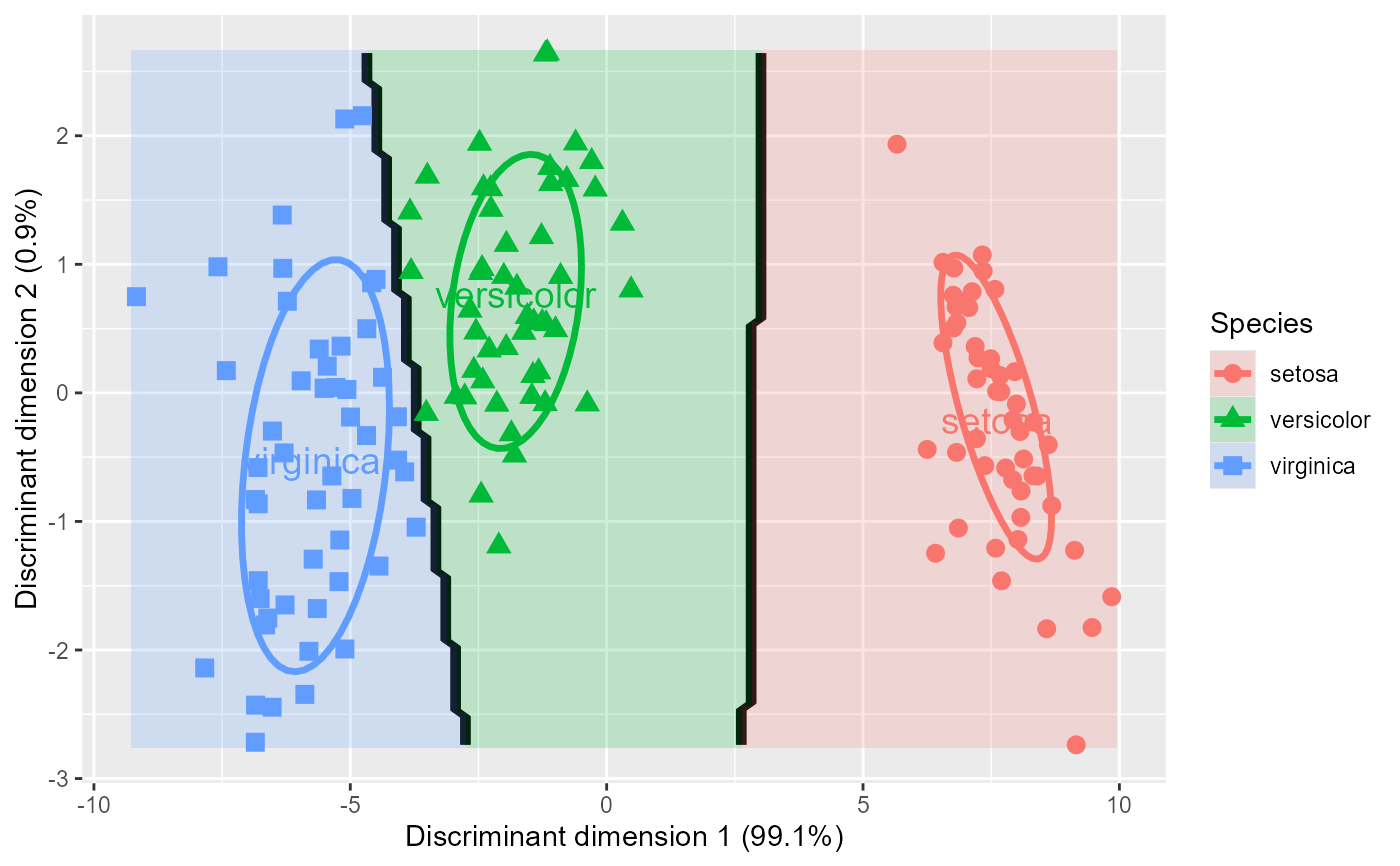
Adds axis labels showing the percentage of between-group variance explained by each dimension
This is useful for visualizing the discriminant analysis results in the space where groups are maximally separated. The axis labels automatically include the variance percentages, e.g., "Discriminant dimension 1 (86.5%)".
References
Fox, J. (1987). Effect Displays for Generalized Linear Models. In C. C. Clogg (Ed.), Sociological Methodology, 1987 (pp. 347–361). Jossey-Bass
See also
klaR::partimat() for pairwise discriminant plots, but with little control of plot details
Author
Original code by Oliver on SO https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63782598/quadratic-discriminant-analysis-qda-plot-in-r.
Generalized by Michael Friendly
Examples
library(MASS)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
iris.lda <- lda(Species ~ ., iris)
# formula call: y ~ x
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width)
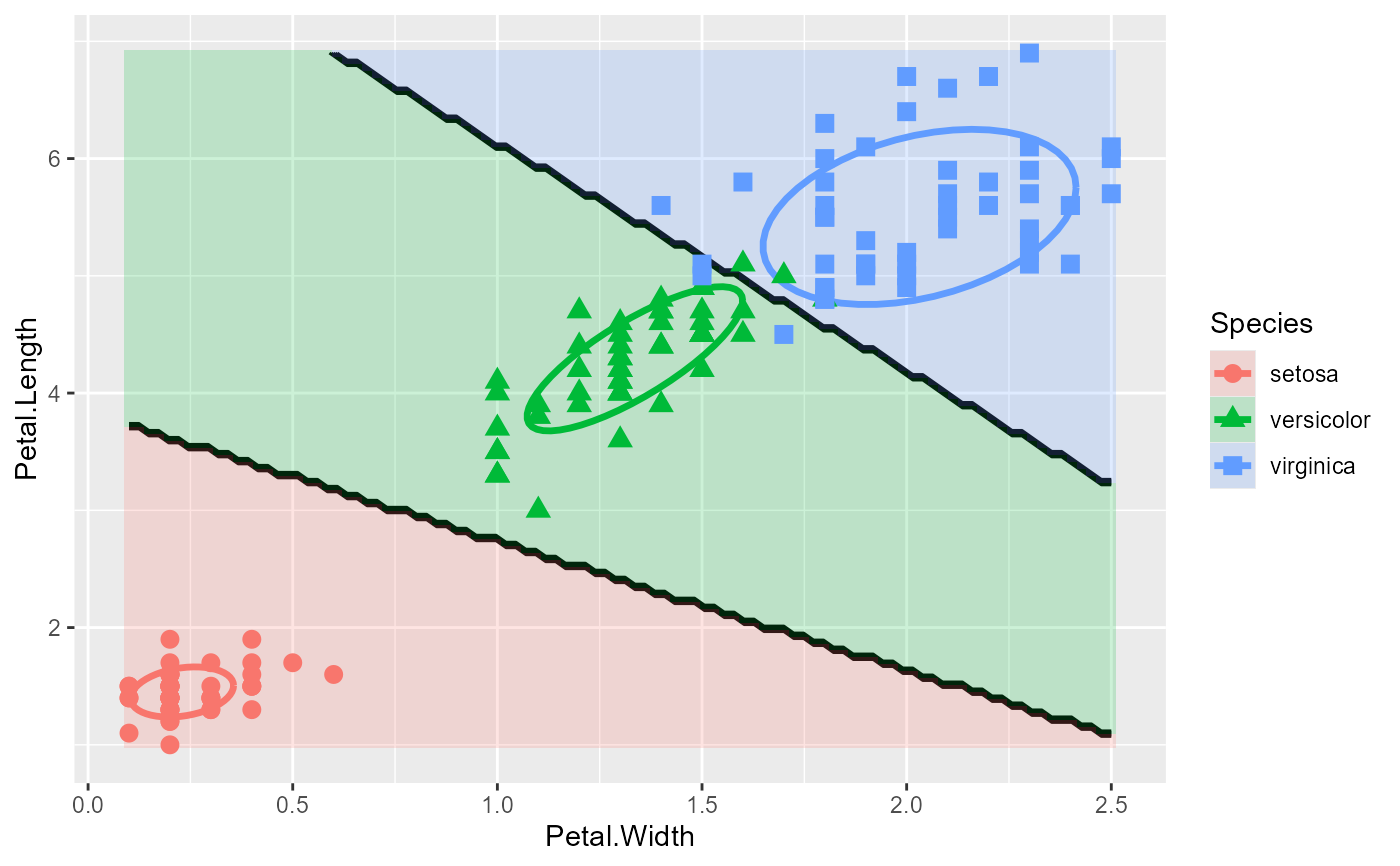
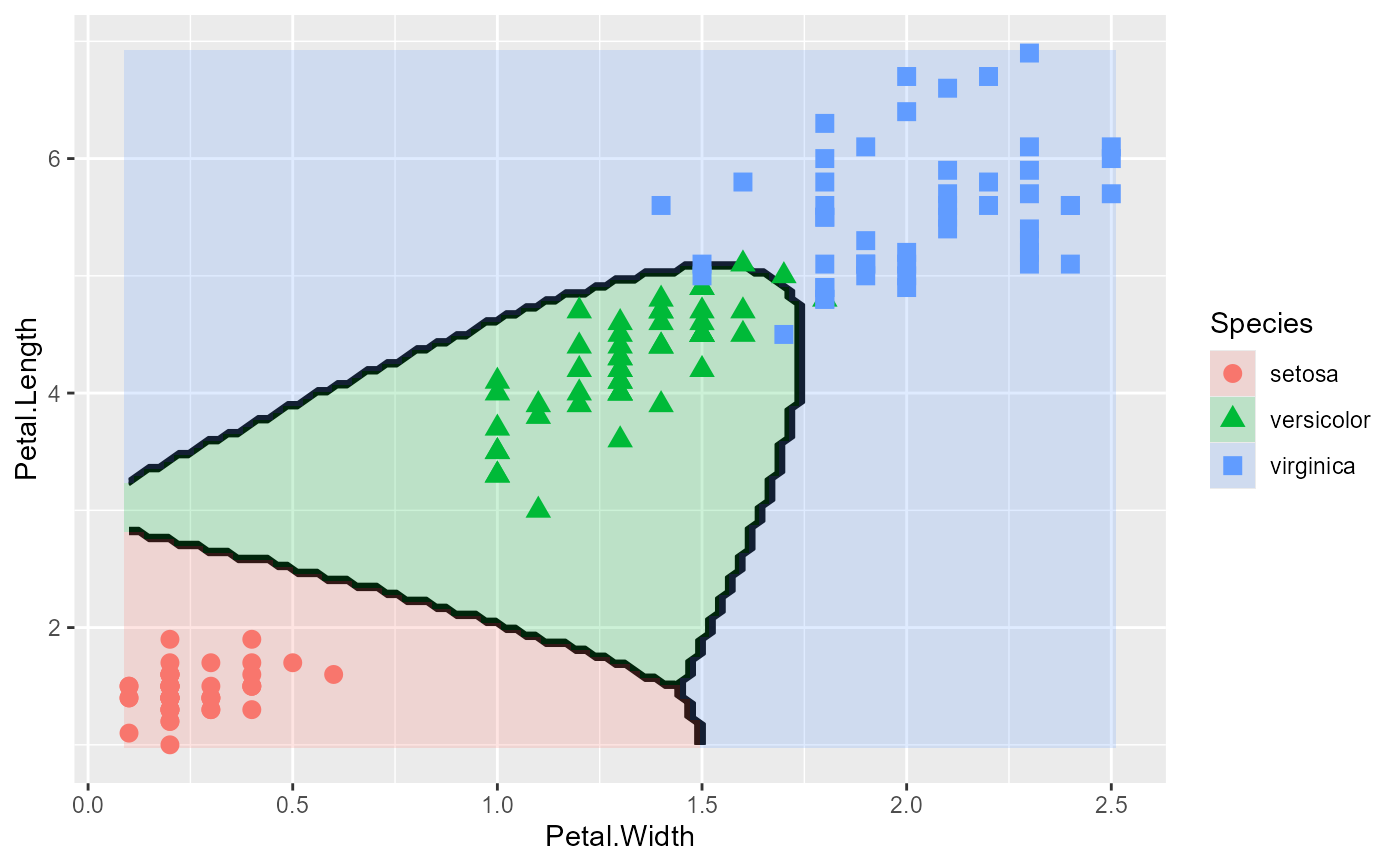
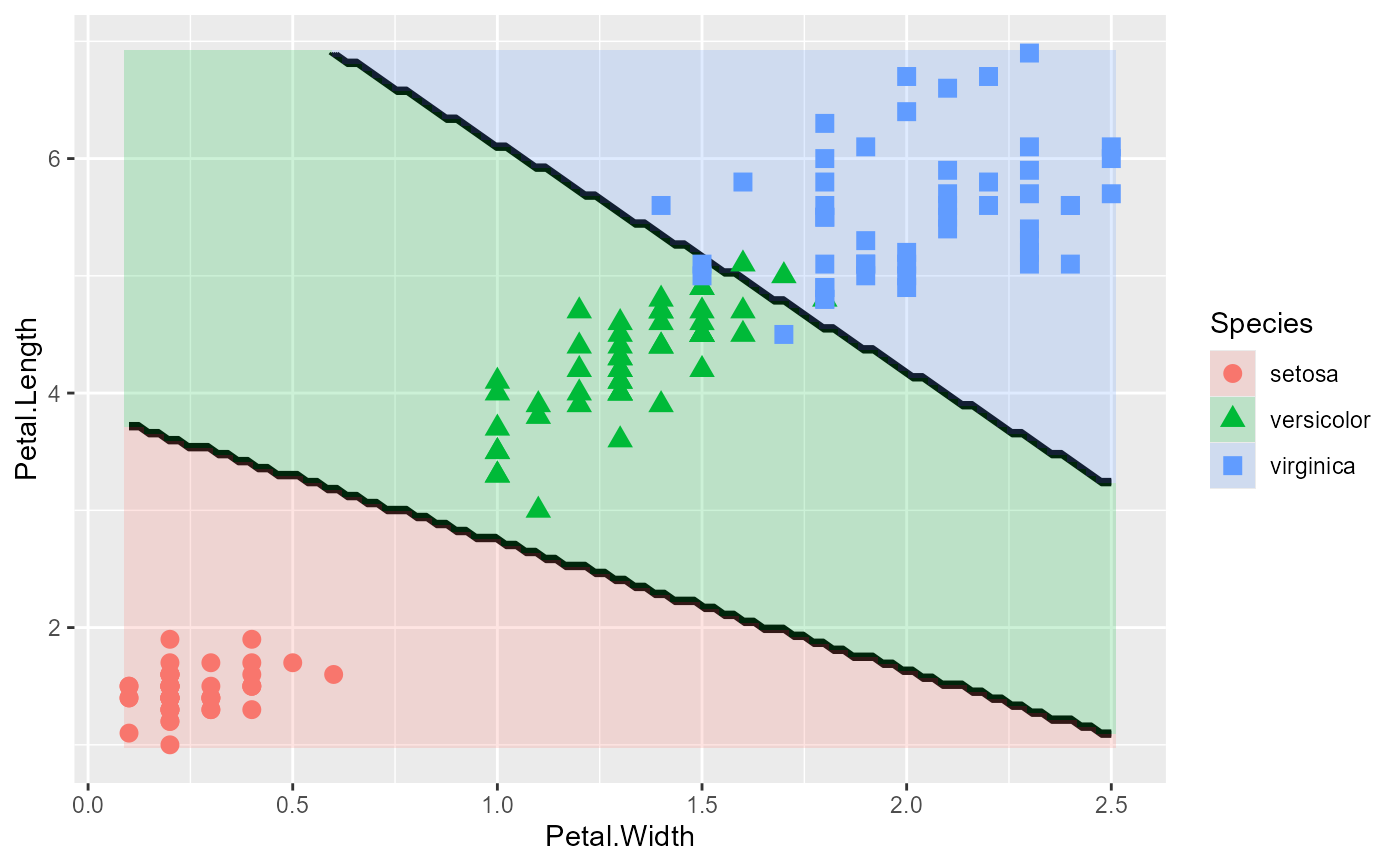 # add data ellipses
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
ellipse = TRUE)
# add data ellipses
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
ellipse = TRUE)
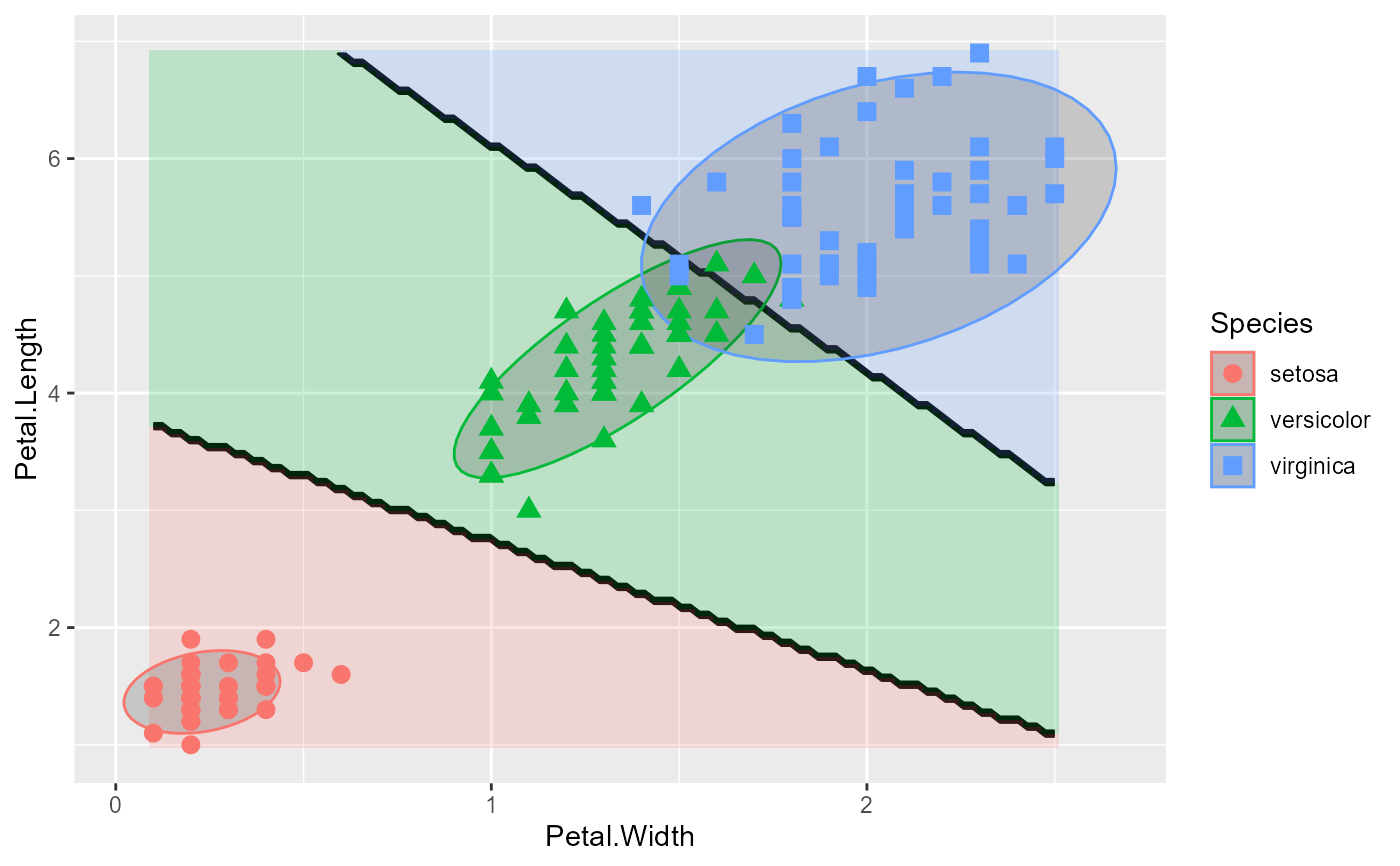
 # add filled ellipses with transparency
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
ellipse = TRUE,
ellipse.args = list(geom = "polygon", alpha = 0.2))
# add filled ellipses with transparency
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
ellipse = TRUE,
ellipse.args = list(geom = "polygon", alpha = 0.2))
 # customize ellipse level and line thickness
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
ellipse = TRUE,
ellipse.args = list(level = 0.95, linewidth = 2))
# customize ellipse level and line thickness
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
ellipse = TRUE,
ellipse.args = list(level = 0.95, linewidth = 2))
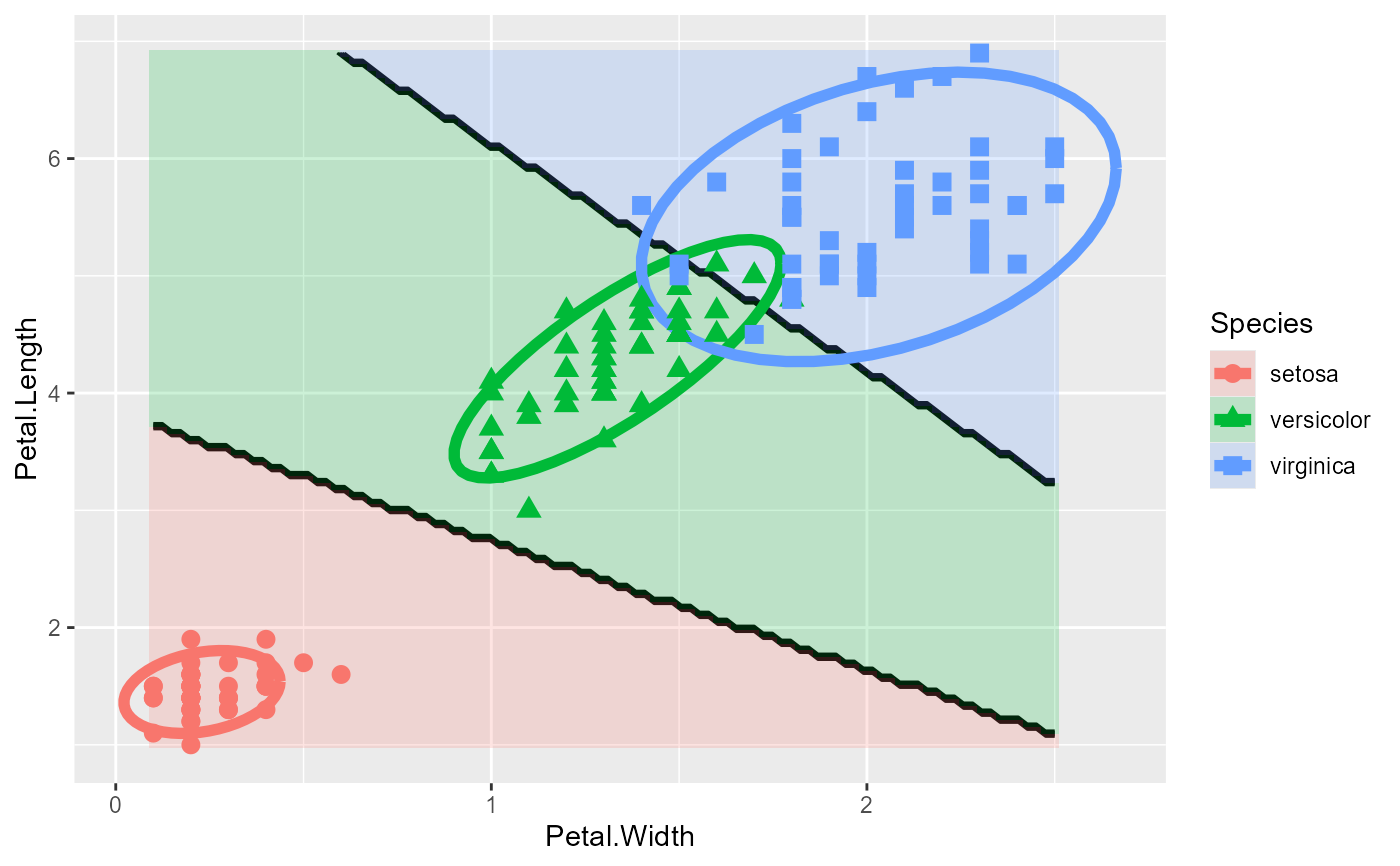 # Define custom colors and shapes, modify theme() and legend.position
iris.colors <- c("red", "darkgreen", "blue")
iris.pch <- 15:17
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width) +
scale_color_manual(values = iris.colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = iris.colors) +
scale_shape_manual(values = iris.pch) +
theme_bw(base_size = 14) +
theme(legend.position = "inside",
legend.position.inside = c(.8, .25))
# Define custom colors and shapes, modify theme() and legend.position
iris.colors <- c("red", "darkgreen", "blue")
iris.pch <- 15:17
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width) +
scale_color_manual(values = iris.colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = iris.colors) +
scale_shape_manual(values = iris.pch) +
theme_bw(base_size = 14) +
theme(legend.position = "inside",
legend.position.inside = c(.8, .25))
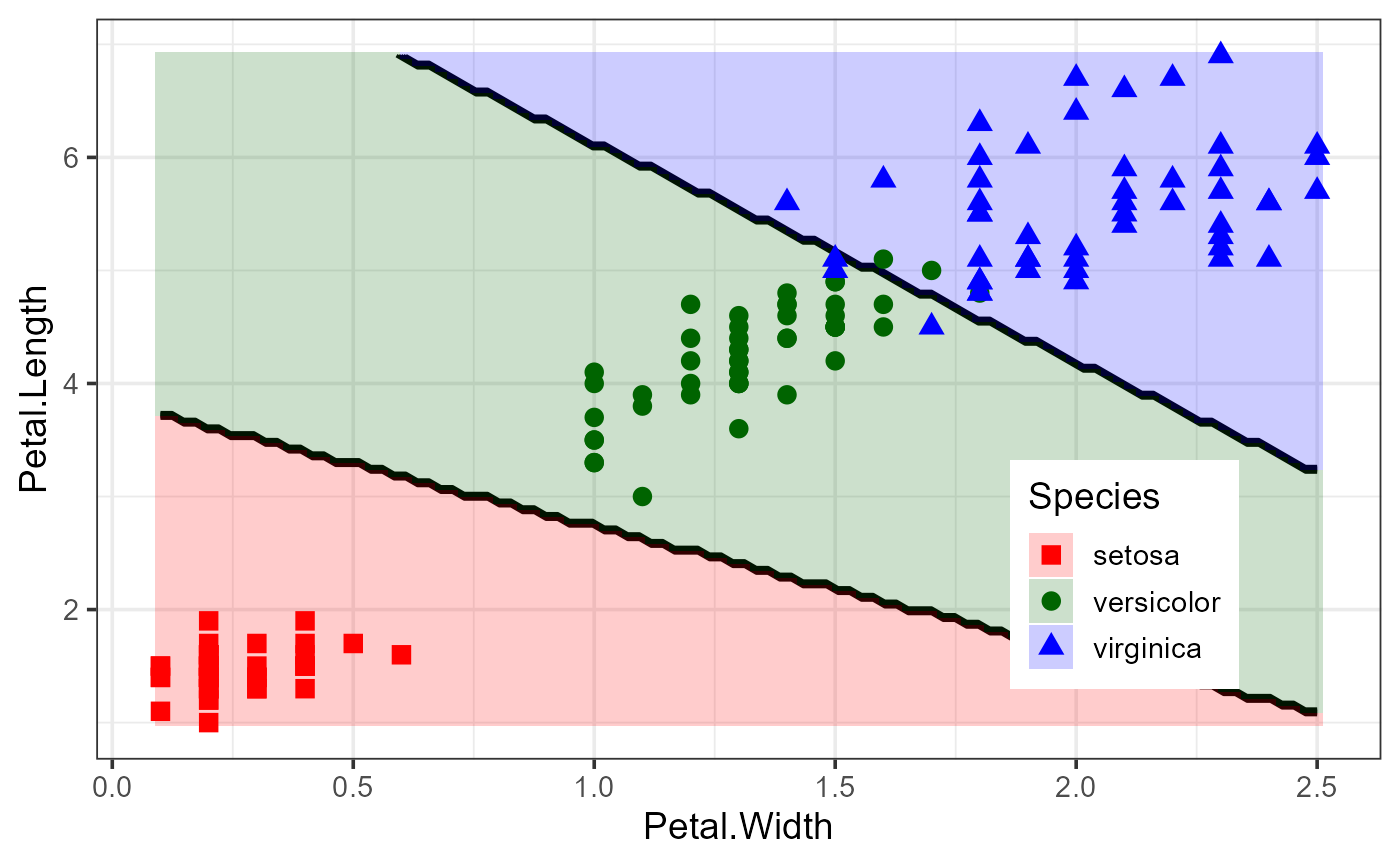 # Quadratic discriminant analysis gives quite a different result
iris.qda <- qda(Species ~ ., iris)
plot_discrim(iris.qda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width)
# Quadratic discriminant analysis gives quite a different result
iris.qda <- qda(Species ~ ., iris)
plot_discrim(iris.qda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width)
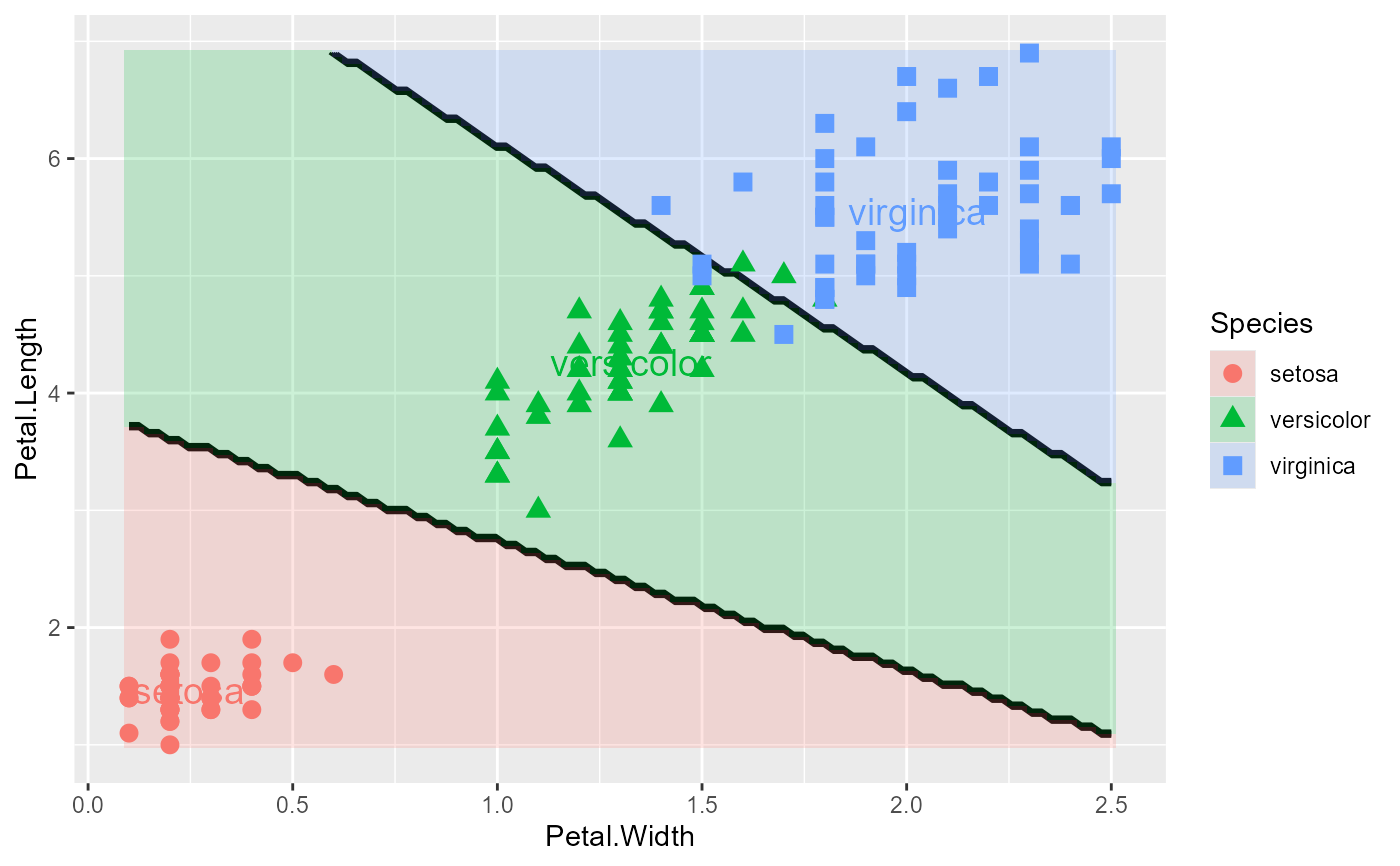
 # Add class labels at group means
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
labels = TRUE)
# Add class labels at group means
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
labels = TRUE)
 # Add labels with custom styling
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
labels = TRUE,
labels.args = list(geom = "label", size = 6, fontface = "bold"))
# Add labels with custom styling
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
labels = TRUE,
labels.args = list(geom = "label", size = 6, fontface = "bold"))
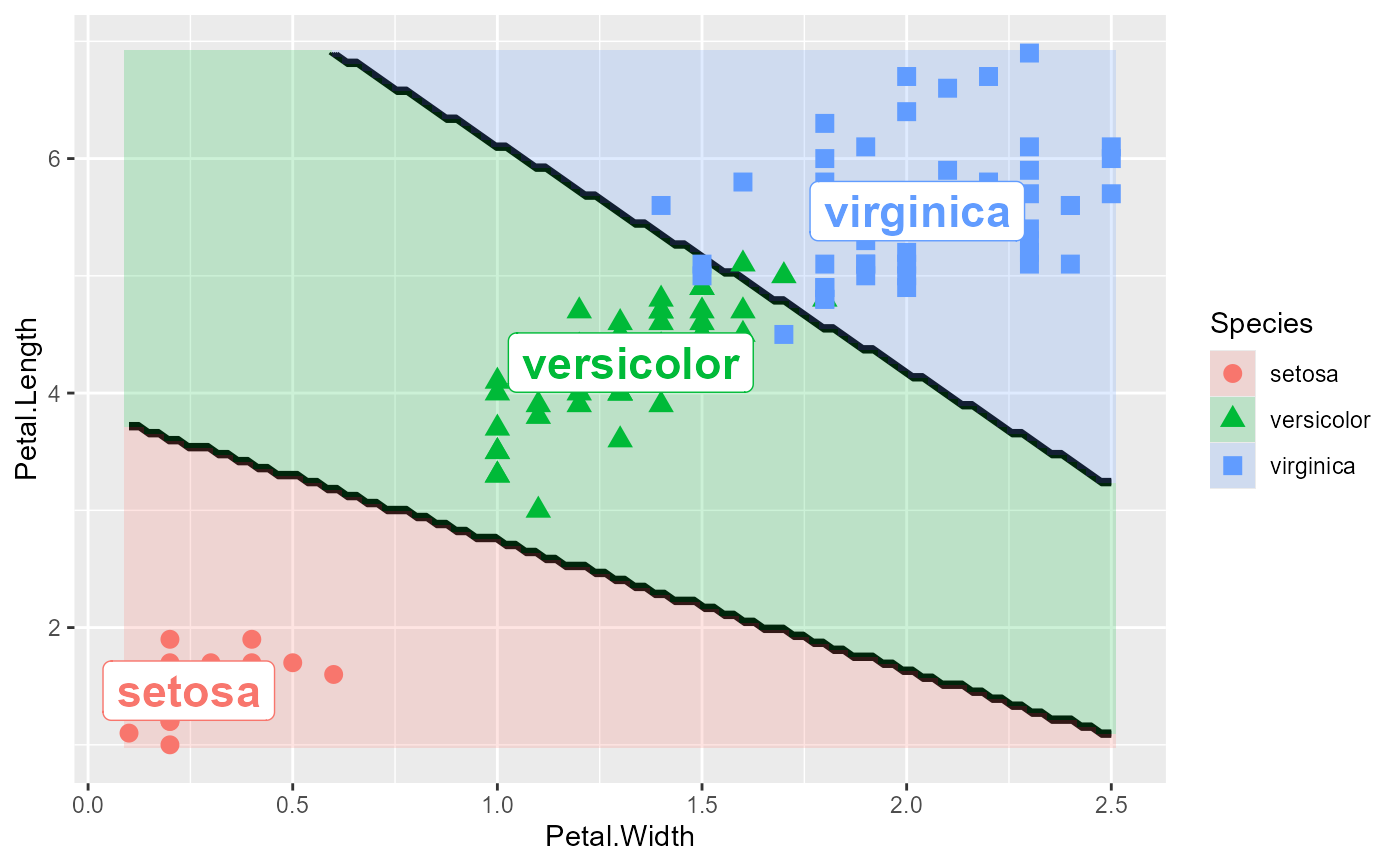 # Add labels with position adjustments
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
labels = TRUE,
labels.args = list(nudge_y = 0.1, size = 5))
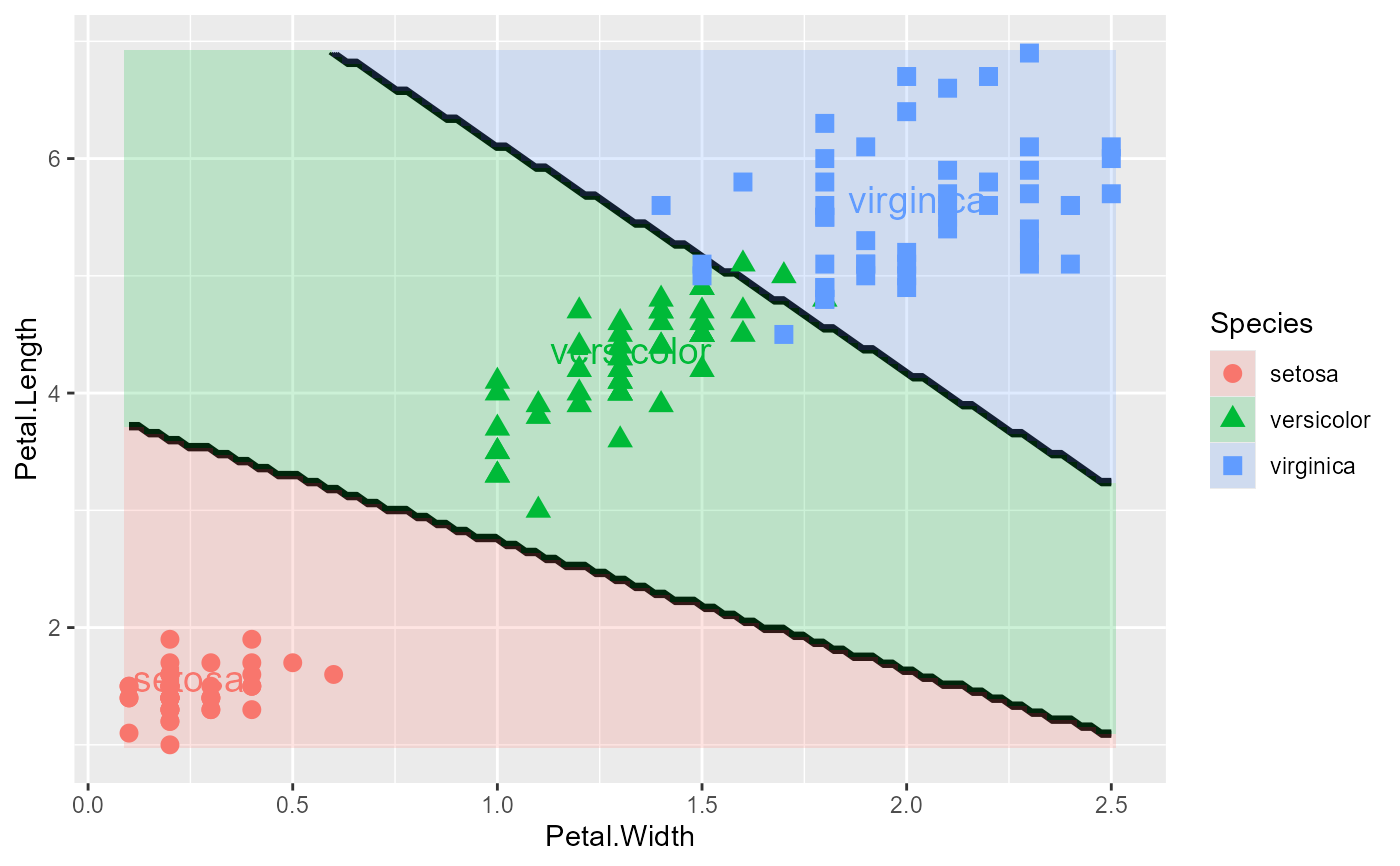
# Add labels with position adjustments
plot_discrim(iris.lda, Petal.Length ~ Petal.Width,
labels = TRUE,
labels.args = list(nudge_y = 0.1, size = 5))
 # Plot in discriminant space with automatic variance labels
plot_discrim(iris.lda, LD2 ~ LD1,
ellipse = TRUE,
labels = TRUE)
# Plot in discriminant space with automatic variance labels
plot_discrim(iris.lda, LD2 ~ LD1,
ellipse = TRUE,
labels = TRUE)