The function vif.ridge calculates variance inflation factors for the
predictors in a set of ridge regression models indexed by the
tuning/shrinkage factor, returning one row for each value of the \(\lambda\) parameter.
Variance inflation factors are calculated using the simplified formulation in Fox & Monette (1992).
The plot.vif.ridge method plots variance inflation factors for a "vif.ridge" object
in a similar style to what is provided by traceplot. That is, it plots the VIF for each
coefficient in the model against either the ridge \(\lambda\) tuning constant or it's equivalent
effective degrees of freedom.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'ridge'
vif(mod, ...)
# S3 method for class 'vif.ridge'
print(x, digits = max(4, getOption("digits") - 5), ...)
# S3 method for class 'vif.ridge'
plot(
x,
X = c("lambda", "df"),
col = c("black", "red", "darkgreen", "blue", "darkcyan", "magenta", "brown",
"darkgray"),
pch = c(15:18, 7, 9, 12, 13),
xlab,
ylab = "Variance Inflation",
xlim,
ylim,
...
)Arguments
- mod
A
"ridge"object computed byridge- ...
Other arguments passed to methods
- x
A
ridgeobject, as fit byridge- digits
Number of digits to display in the
printmethod- X
What to plot as the horizontal coordinate, one of
c("lambda", "df")- col
A numeric or character vector giving the colors used to plot the ridge trace curves. Recycled as necessary.
- pch
Vector of plotting characters used to plot the ridge trace curves. Recycled as necessary.
- xlab
Label for horizontal axis
- ylab
Label for vertical axis
- xlim, ylim
x, y limits for the plot. You may need to adjust these to allow for the variable labels.
Value
vif returns a "vif.ridge" object, which is a list of four components
- vif
a data frame of the same size and shape as
coef{mod}. The columns correspond to the predictors in the model and the rows correspond to the values oflambdain ridge estimation.- lambda
the vector of ridge constants from the original call to
ridge- df
the vector of effective degrees of freedom corresponding to
lambda- criteria
the optimal values of
lambda
References
Fox, J. and Monette, G. (1992). Generalized collinearity diagnostics. JASA, 87, 178-183, doi:10.1080/01621459.1992.10475190 .
Examples
data(longley)
lmod <- lm(Employed ~ GNP + Unemployed + Armed.Forces + Population +
Year + GNP.deflator, data=longley)
vif(lmod)
#> GNP Unemployed Armed.Forces Population Year GNP.deflator
#> 1788.51348 33.61889 3.58893 399.15102 758.98060 135.53244
lambda <- c(0, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.08)
lridge <- ridge(Employed ~ GNP + Unemployed + Armed.Forces +
Population + Year + GNP.deflator,
data=longley, lambda=lambda)
coef(lridge)
#> GNP Unemployed Armed.Forces Population Year GNP.deflator
#> 0.000 -3.4471925 -1.827886 -0.6962102 -0.34419721 8.431972 0.15737965
#> 0.005 -1.0424783 -1.491395 -0.6234680 -0.93558040 6.566532 -0.04175039
#> 0.010 -0.1797967 -1.361047 -0.5881396 -1.00316772 5.656287 -0.02612152
#> 0.020 0.4994945 -1.245137 -0.5476331 -0.86755299 4.626116 0.09766305
#> 0.040 0.9059471 -1.155229 -0.5039108 -0.52347060 3.576502 0.32123994
#> 0.080 1.0907048 -1.086421 -0.4582525 -0.08596324 2.641649 0.57025165
# get VIFs for the shrunk estimates
vridge <- vif(lridge)
vridge
#> Variance inflaction factors:
#> GNP Unemployed Armed.Forces Population Year GNP.deflator
#> 0.000 1788.51 33.619 3.589 399.15 758.98 135.53
#> 0.005 540.04 12.118 2.921 193.30 336.15 90.63
#> 0.010 259.00 7.284 2.733 134.42 218.84 74.79
#> 0.020 101.12 4.573 2.578 87.29 128.82 58.94
#> 0.040 34.43 3.422 2.441 52.22 66.31 43.56
#> 0.080 11.28 2.994 2.301 28.59 28.82 29.52
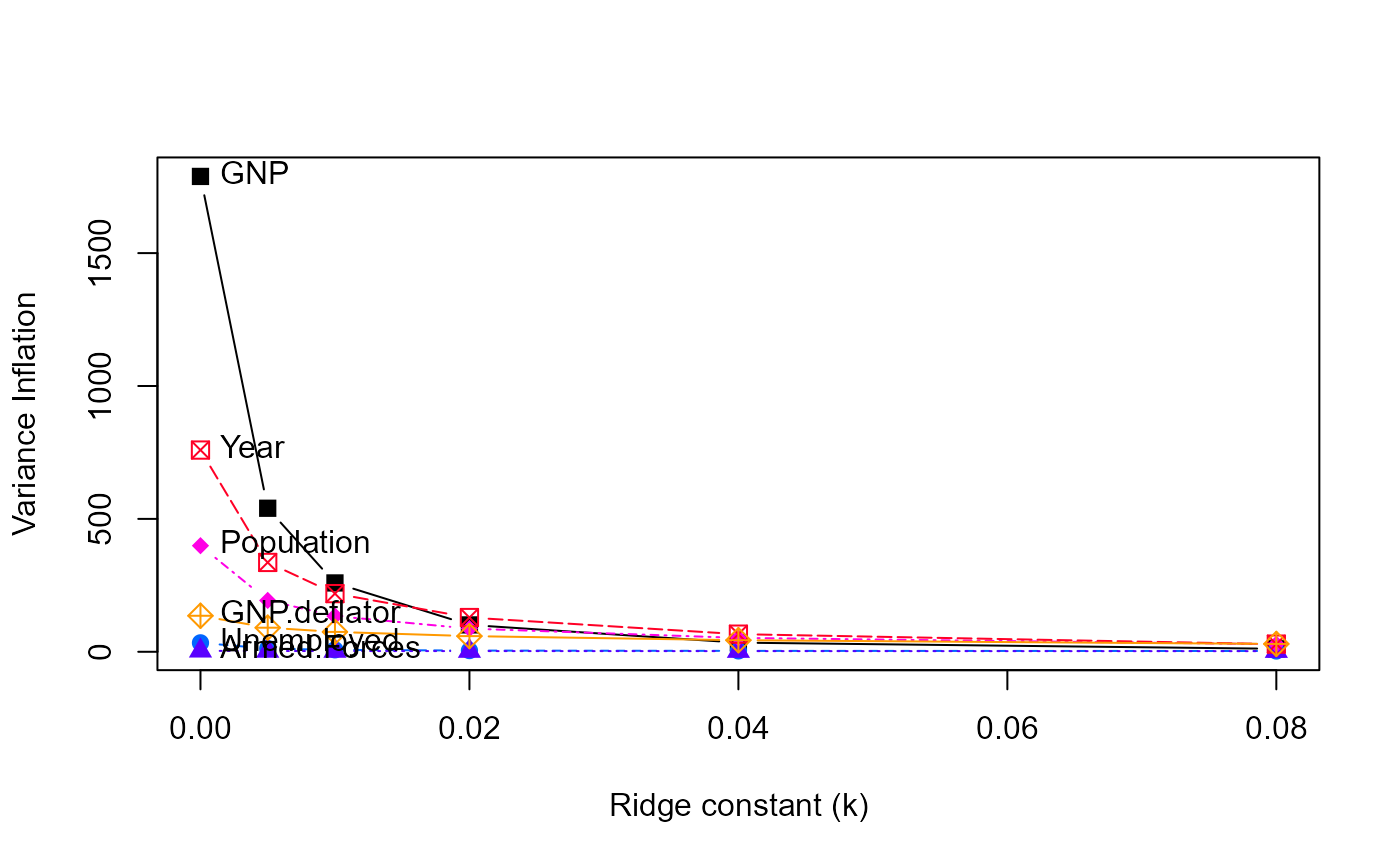
# plot VIFs
pch <- c(15:18, 7, 9)
clr <- c("black", rainbow(5, start=.6, end=.1))
### Transition examples, because the vif() method now returns a list structure
### rather than a data.frame
vr <- vridge$vif
matplot(rownames(vr), vr, type='b',
xlab='Ridge constant (k)', ylab="Variance Inflation",
xlim=c(0, 0.08),
col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2)
text(0.0, vr[1,], colnames(vr), pos=4)
 # matplot(lridge$df, vridge, type='b',
# xlab='Degrees of freedom', ylab="Variance Inflation",
# col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2)
# text(6, vridge[1,], colnames(vridge), pos=2)
# more useful to plot VIF on the sqrt scale
# matplot(rownames(vridge), sqrt(vridge), type='b',
# xlab='Ridge constant (k)', ylab=expression(sqrt(VIF)),
# xlim=c(-0.01, 0.08),
# col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2, cex.lab=1.25)
# text(-0.01, sqrt(vridge[1,]), colnames(vridge), pos=4, cex=1.2)
# matplot(lridge$df, sqrt(vridge), type='b',
# xlab='Degrees of freedom', ylab=expression(sqrt(VIF)),
# col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2, cex.lab=1.25)
# text(6, sqrt(vridge[1,]), colnames(vridge), pos=2, cex=1.2)
# matplot(lridge$df, vridge, type='b',
# xlab='Degrees of freedom', ylab="Variance Inflation",
# col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2)
# text(6, vridge[1,], colnames(vridge), pos=2)
# more useful to plot VIF on the sqrt scale
# matplot(rownames(vridge), sqrt(vridge), type='b',
# xlab='Ridge constant (k)', ylab=expression(sqrt(VIF)),
# xlim=c(-0.01, 0.08),
# col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2, cex.lab=1.25)
# text(-0.01, sqrt(vridge[1,]), colnames(vridge), pos=4, cex=1.2)
# matplot(lridge$df, sqrt(vridge), type='b',
# xlab='Degrees of freedom', ylab=expression(sqrt(VIF)),
# col=clr, pch=pch, cex=1.2, cex.lab=1.25)
# text(6, sqrt(vridge[1,]), colnames(vridge), pos=2, cex=1.2)