This function takes an n-way contingency table and plots mosaics for series of sequential models to the 1-, 2-, ... n-way marginal tables, corresponding to a variety of types of loglinear models.
Usage
seq_mosaic(
x,
panel = mosaic,
type = c("joint", "conditional", "mutual", "markov", "saturated"),
plots = 1:nf,
vorder = 1:nf,
k = NULL,
...
)Arguments
- x
a contingency table in array form, with optional category labels specified in the
dimnames(x)attribute, or else a data.frame in frequency form, with the frequency variable named"Freq".- panel
a
strucplotpanel function, typicallymosaicorsieve. NOT yet implemented.- type
type of sequential model to fit, a character string. One of
"joint","conditional","mutual","markov", or"saturated".- plots
which marginal sub-tables to plot? A vector of a (sub)set of the integers,
1:nfwherenfis the number of factors in the full n-way table.- vorder
order of variables, a permutation of the integers
1:nf, used to reorder the variables in the original table for the purpose of fitting sequential marginal models.- k
conditioning variable(s) for
type="joint","conditional"or Markov chain order fortype="markov"- ...
other arguments passed to
mosaic.
Details
This function produces similar plots to the use of
mosaic.loglmlist, called with the result of
seq_loglm.
References
These functions were inspired by the original SAS implementation of mosaic displays, described in the User's Guide for Mosaics, http://www.datavis.ca/mosaics/mosaics.pdf
See also
loglin-utilities for descriptions of sequential
models, conditional, joint, mutual, ...
loglmlist, mosaic.loglmlist,
seq_loglm
Examples
data(Titanic, package="datasets")
seq_mosaic(Titanic) # models of joint independence, Survived last
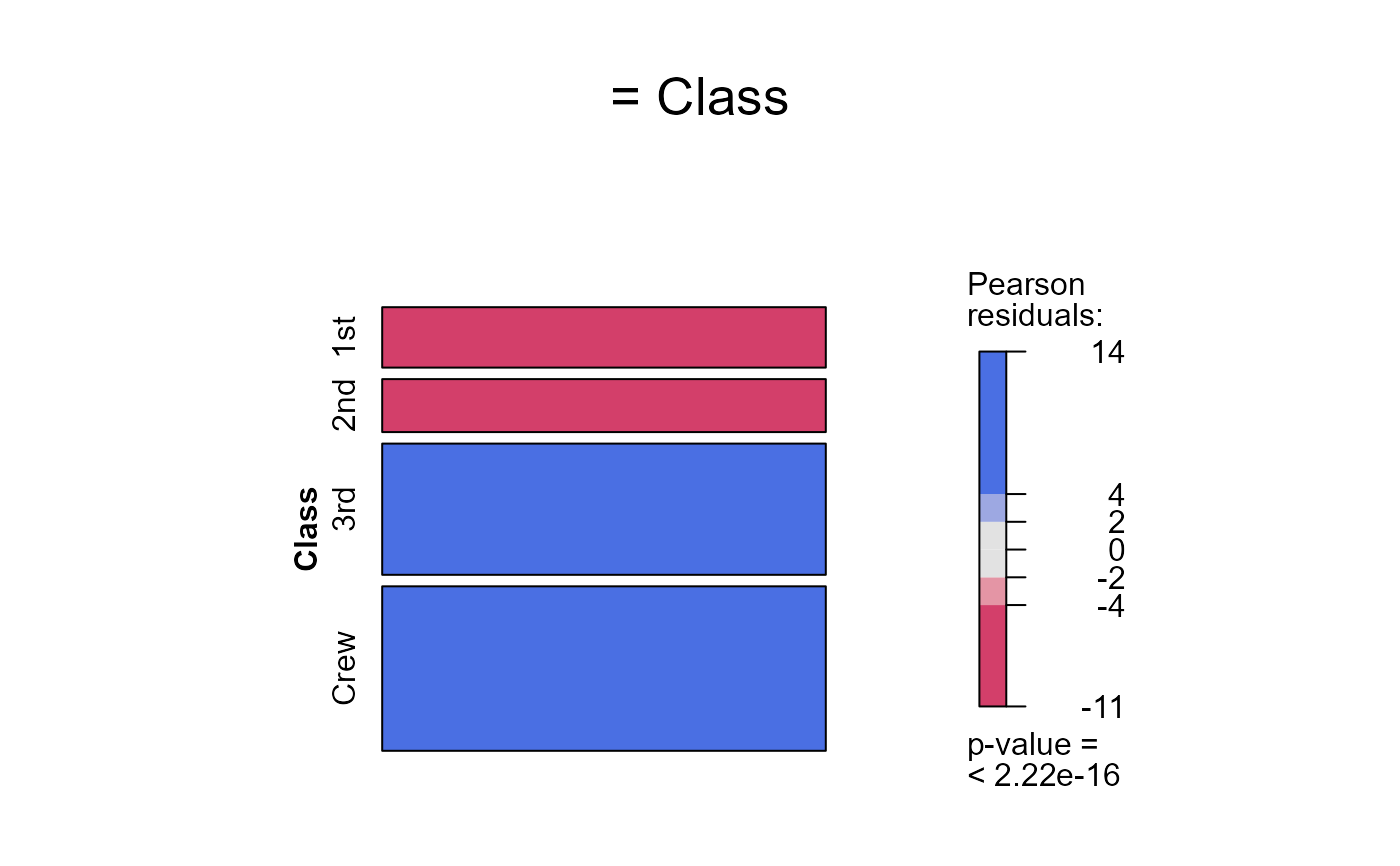
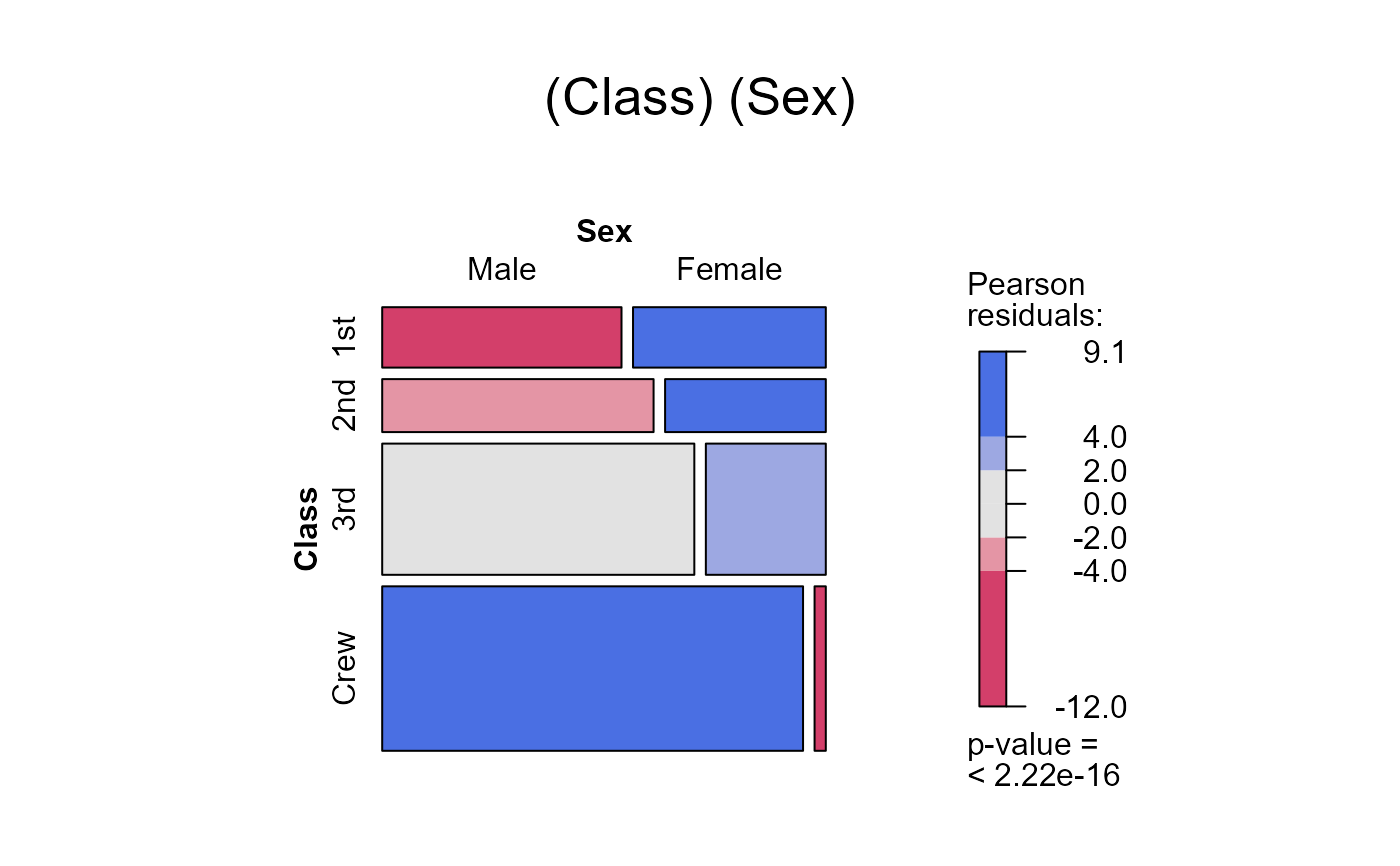
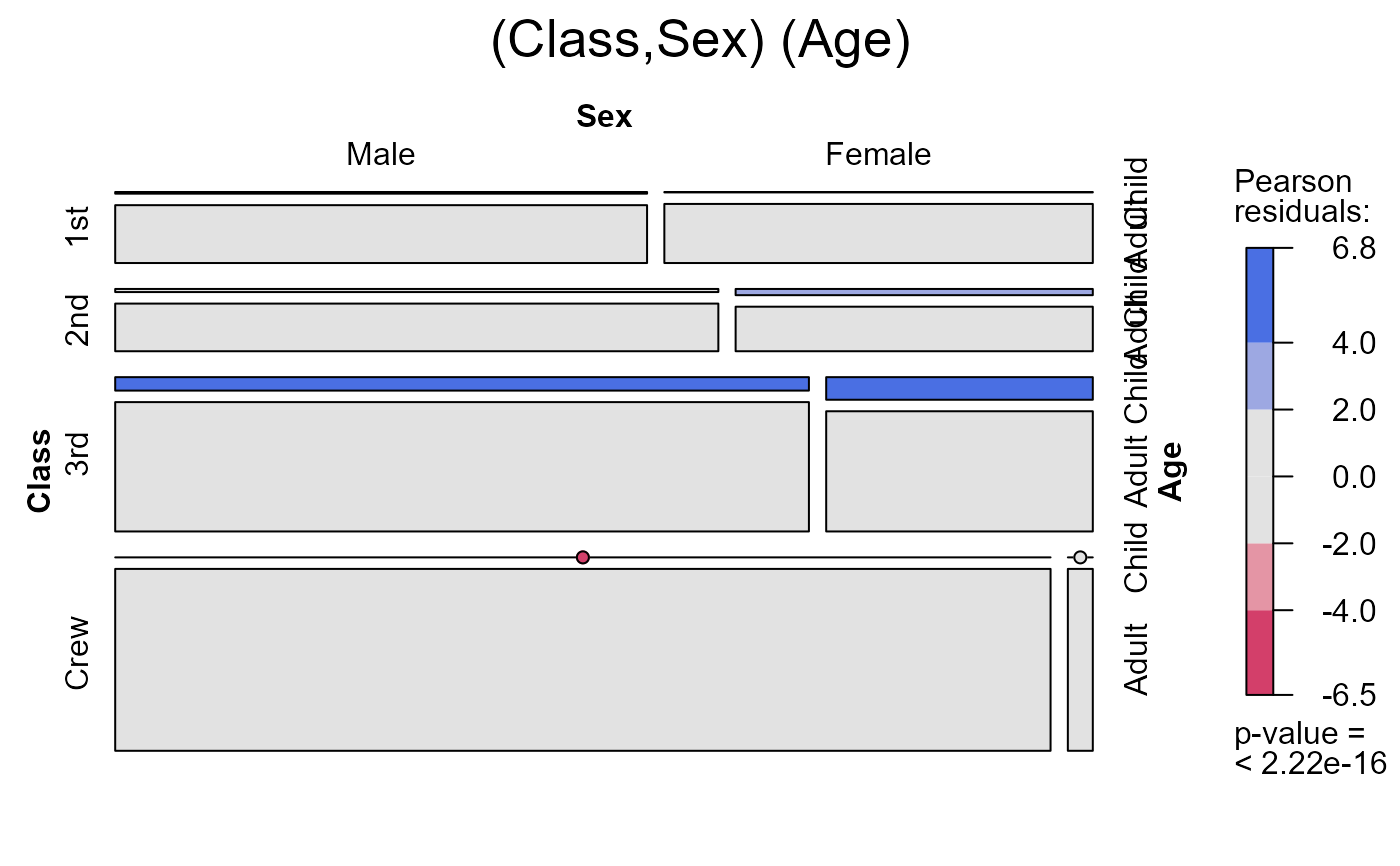
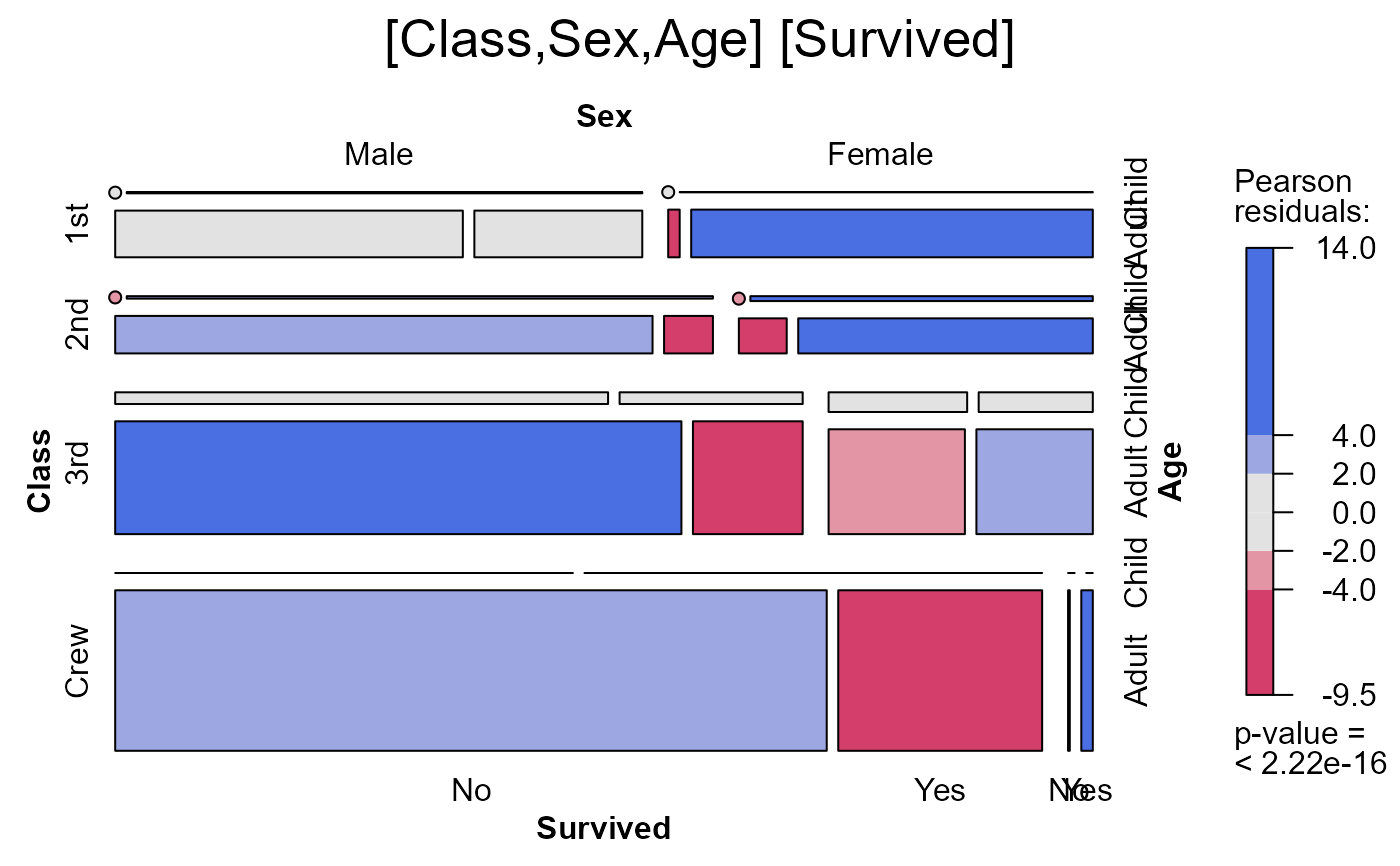 seq_mosaic(Titanic, type="condit")
seq_mosaic(Titanic, type="condit")
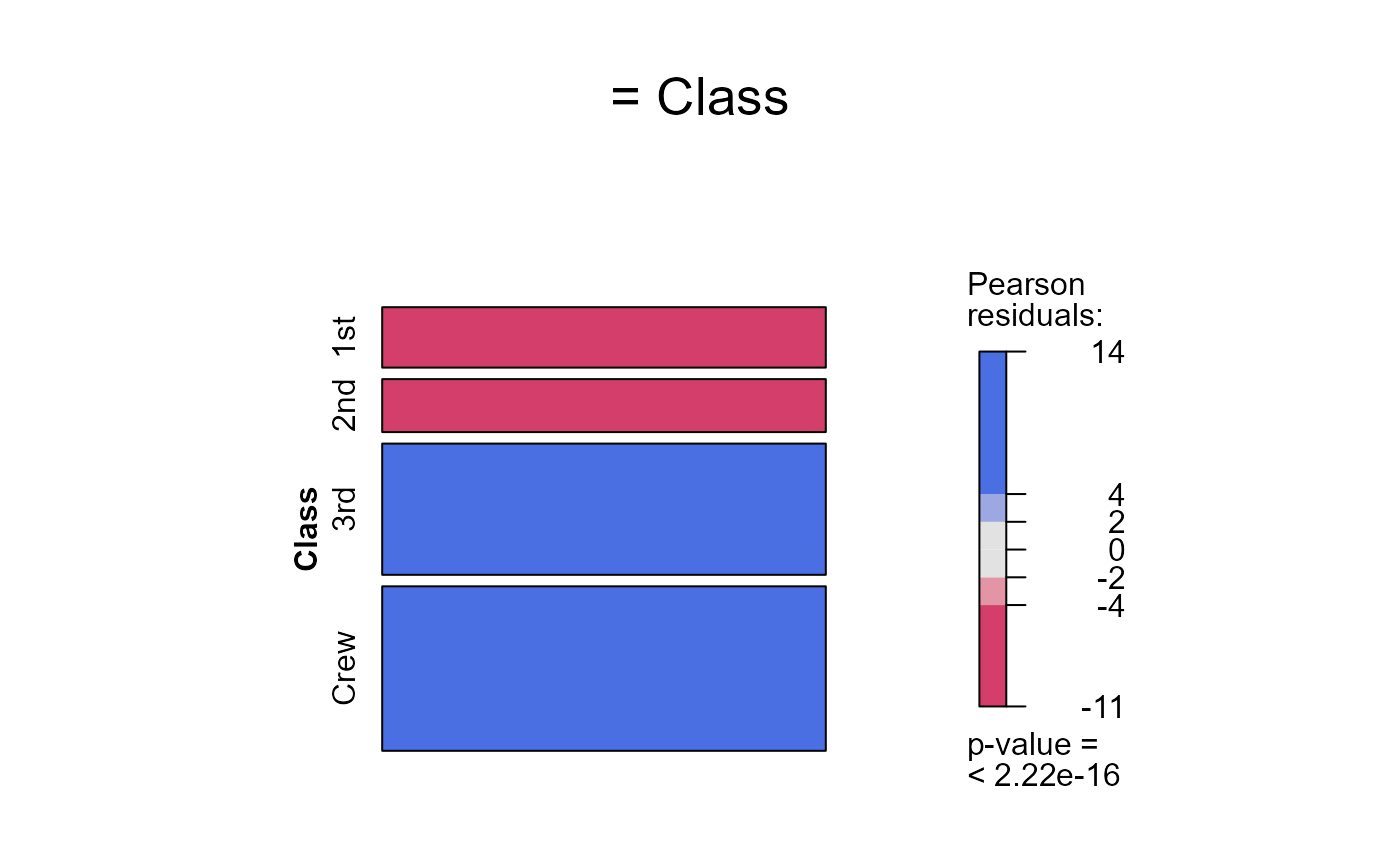
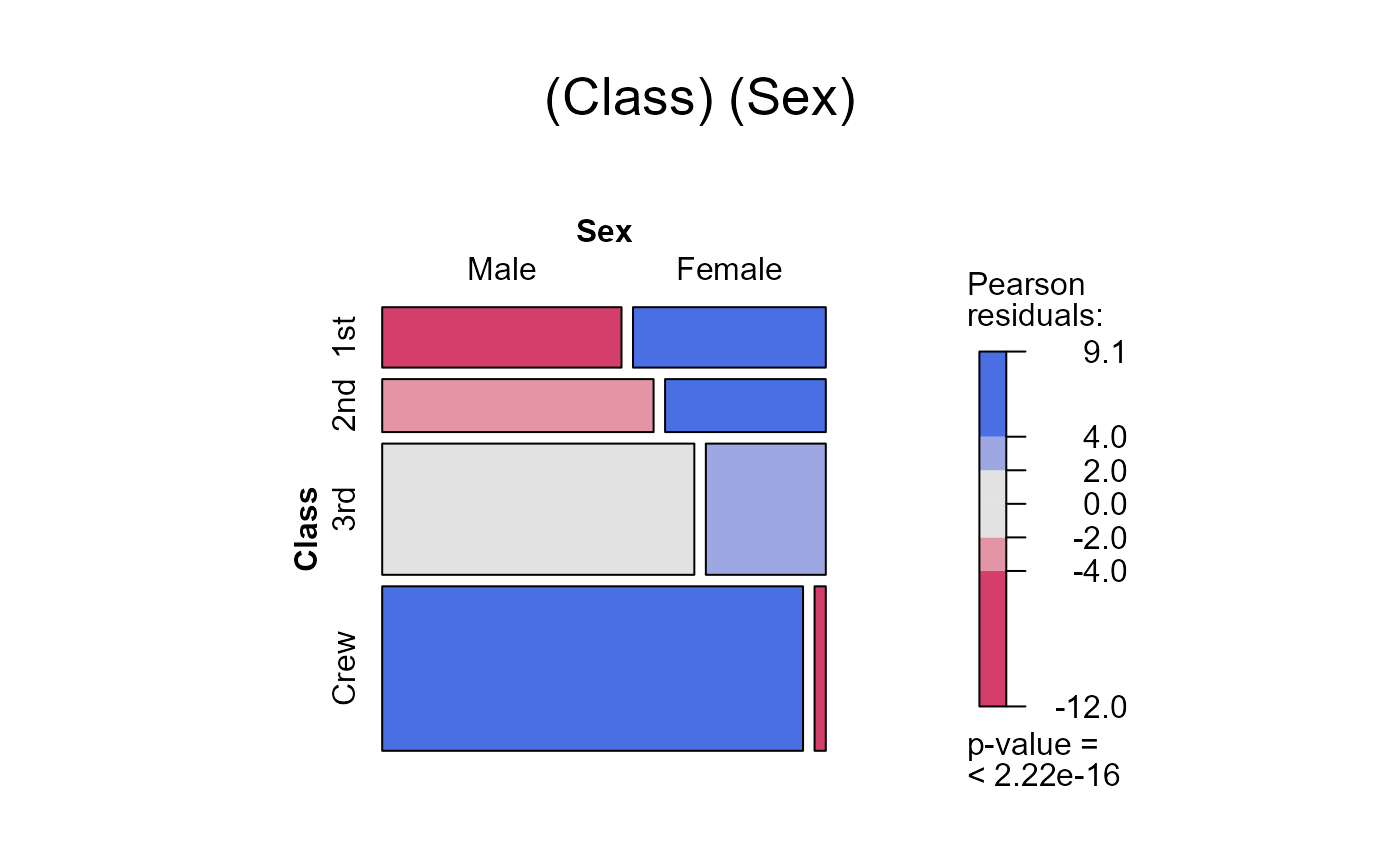
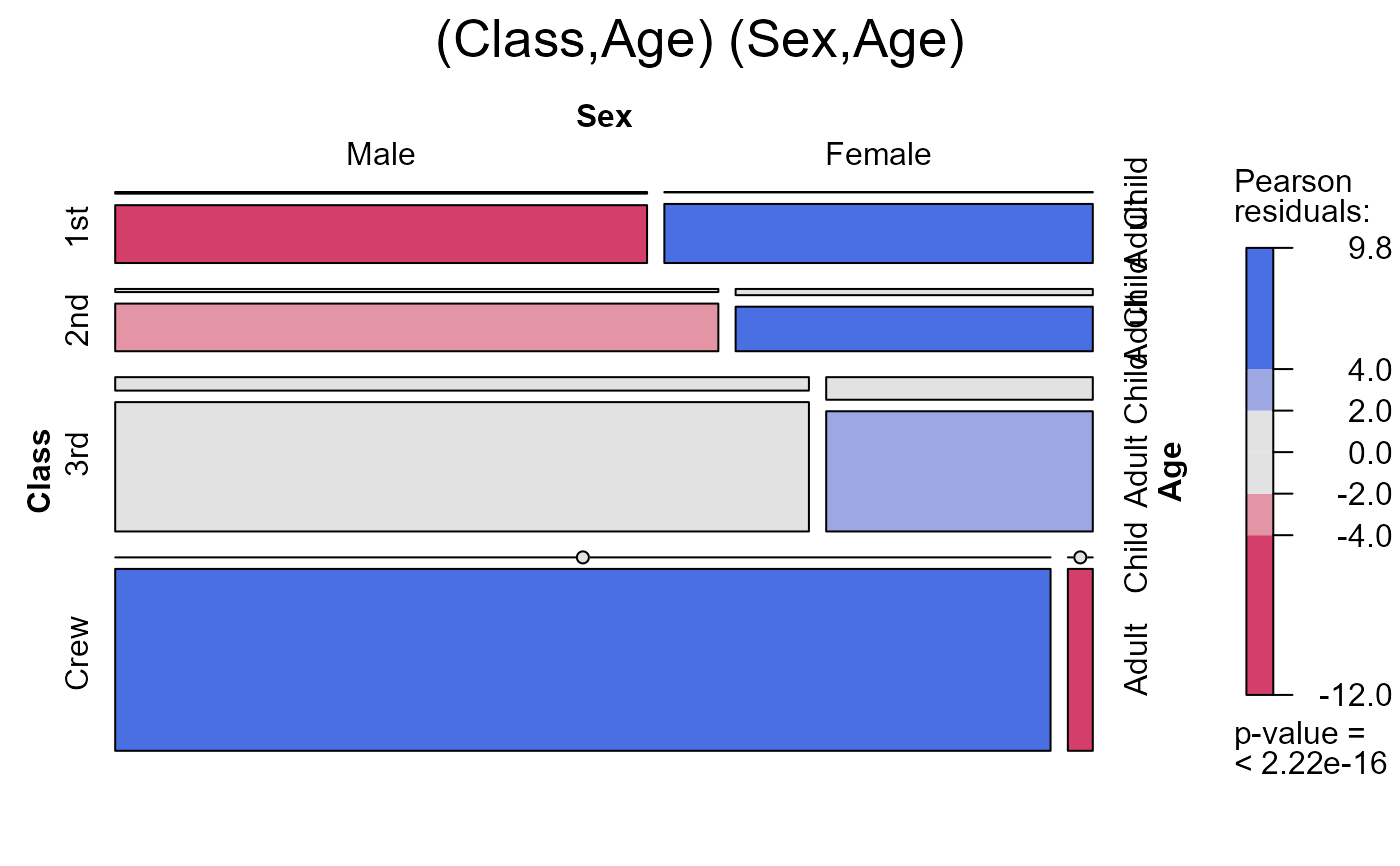
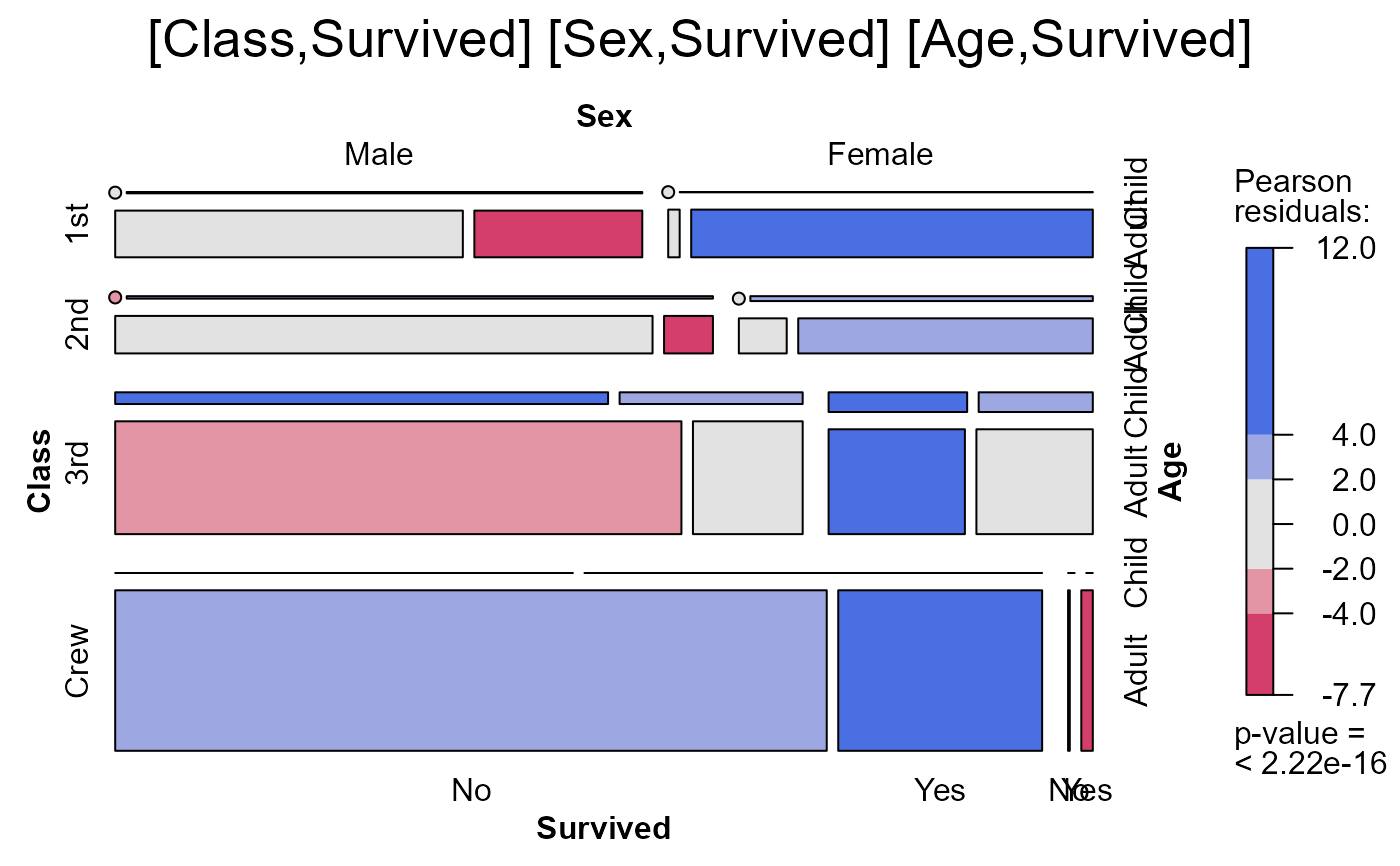 seq_mosaic(Titanic, type="mutual")
seq_mosaic(Titanic, type="mutual")
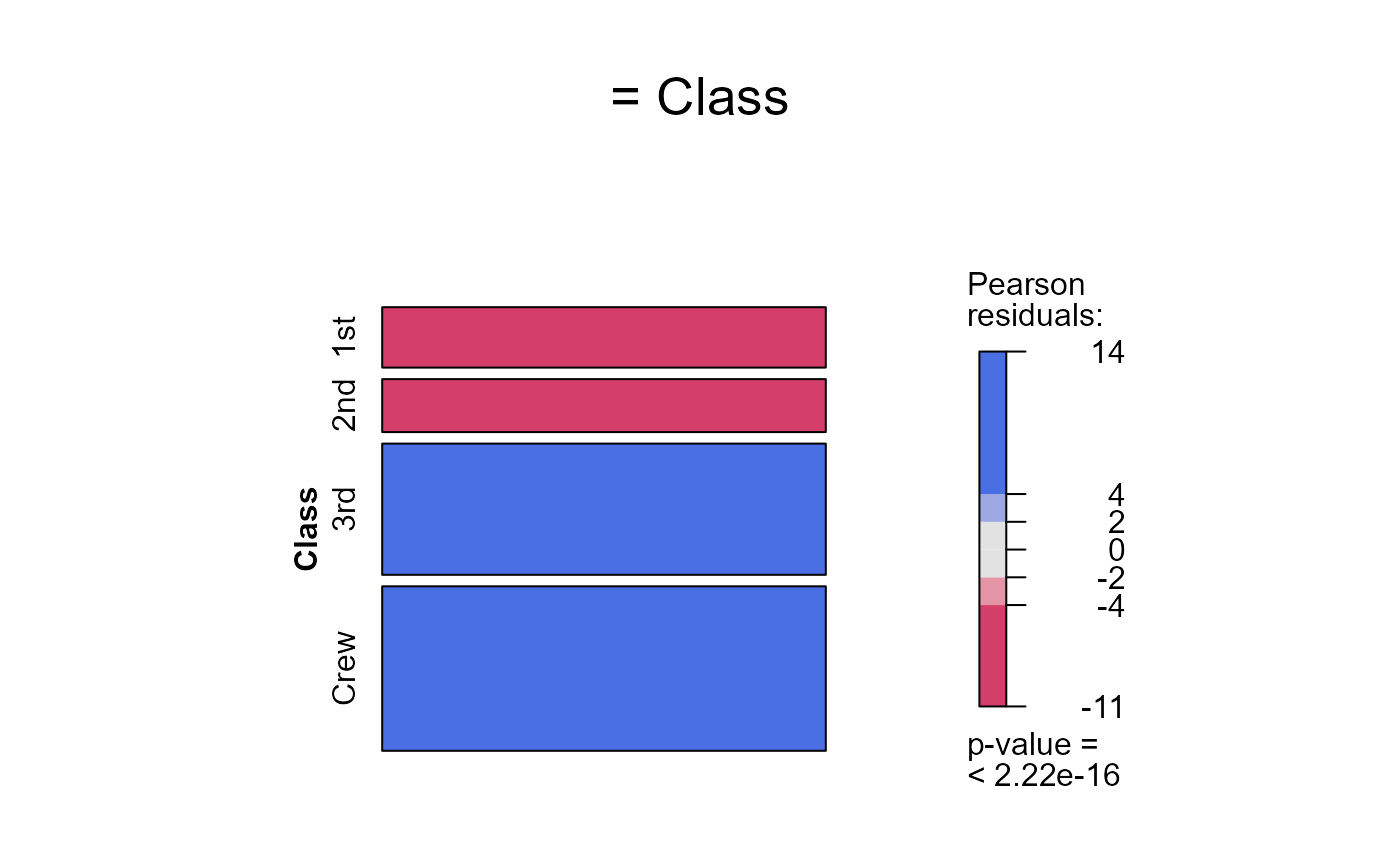
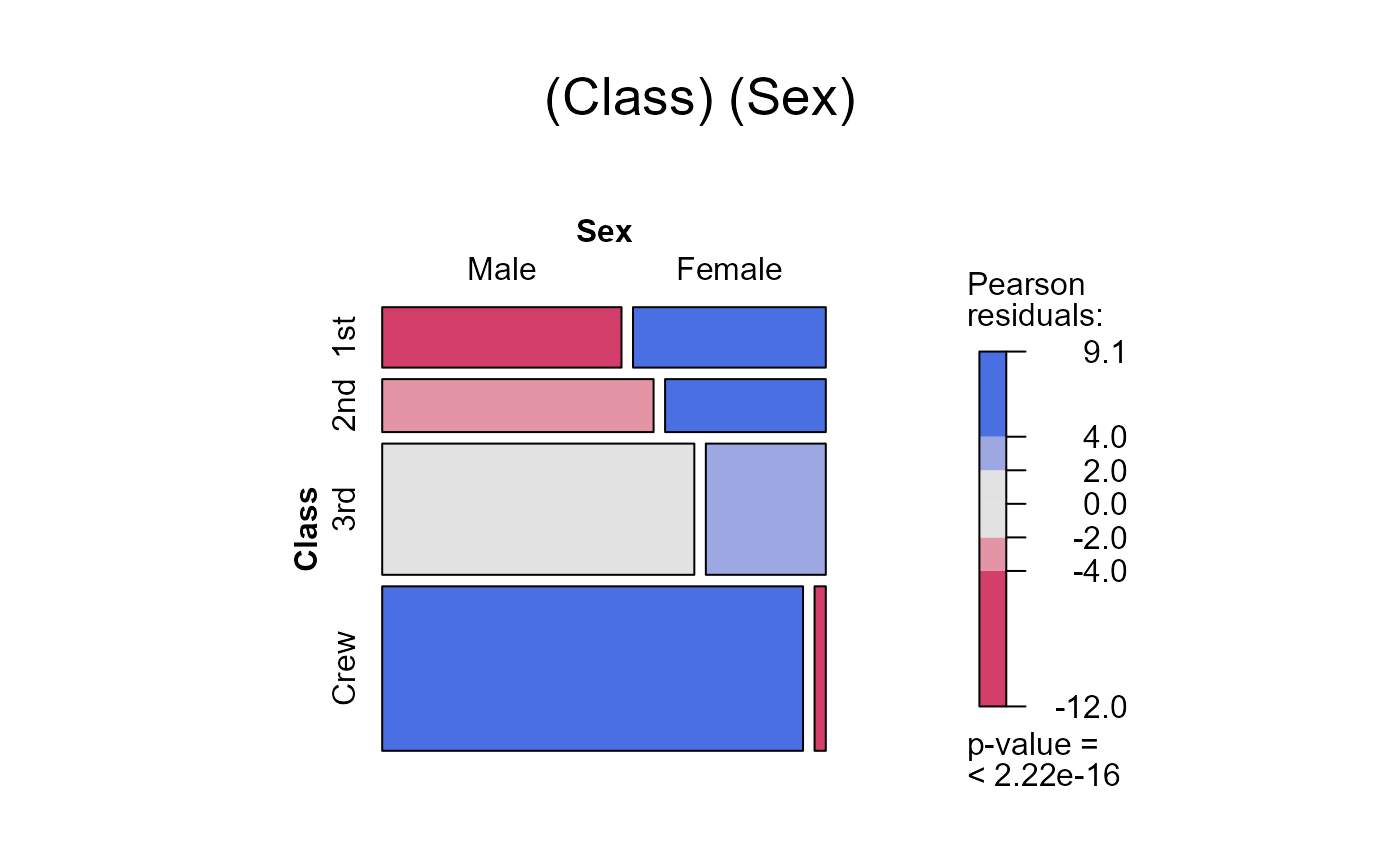
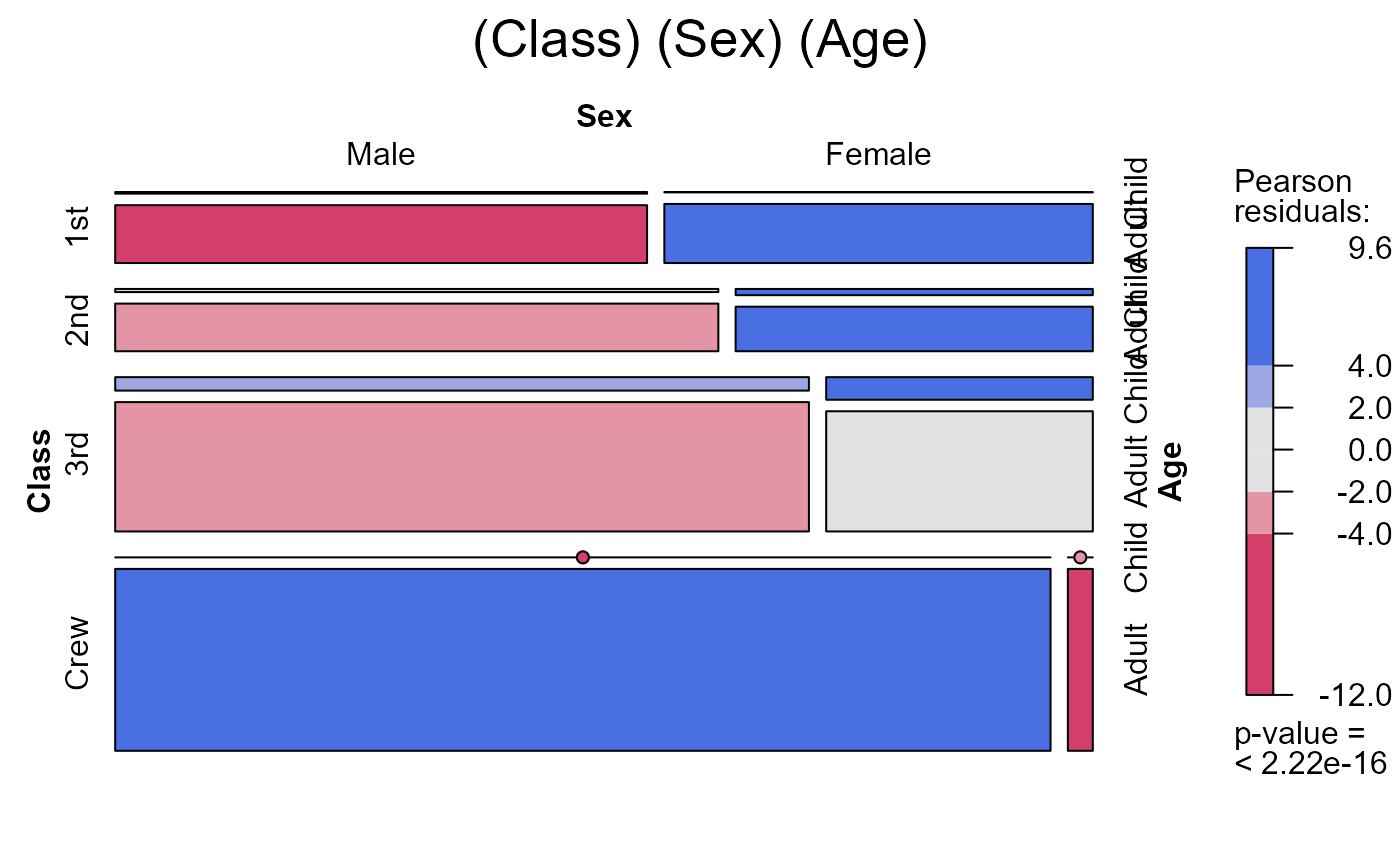
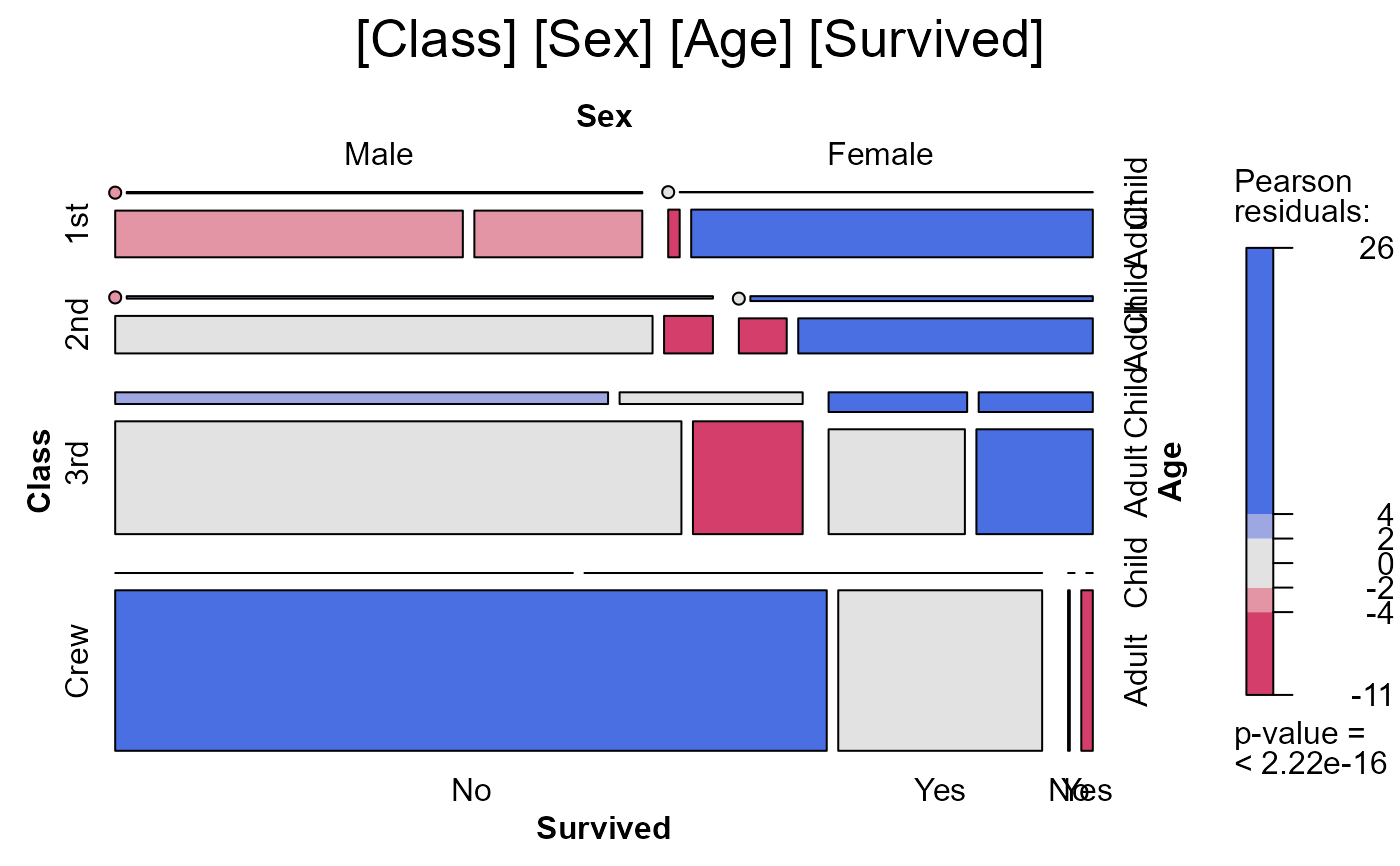 # other panel functions and options: presently BUGGED
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
seq_mosaic(Titanic, type="mutual", panel=sieve,
gp=shading_Friendly, labeling=labeling_values)
} # }
# other panel functions and options: presently BUGGED
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
seq_mosaic(Titanic, type="mutual", panel=sieve,
gp=shading_Friendly, labeling=labeling_values)
} # }
